Recent Posts
Search Topic
The Circle of Fifths is a visual music tool represents to describes the relationships between the 12 tones of the chromatic scale, their corresponding key signatures, and the associated major and minor keys. The reason it’s called the circle of fifths is because of the interval relationships between each key signature. The Pythagorean Circle was the pillar of the Circle of Fifths. But Nikolay Diletsky in the year 1670 first invented the Circle of Fifths. Many modifications were made to improve the theory. Until German musician, Johann David Heinichen in 1728 was created today’s improvised version.
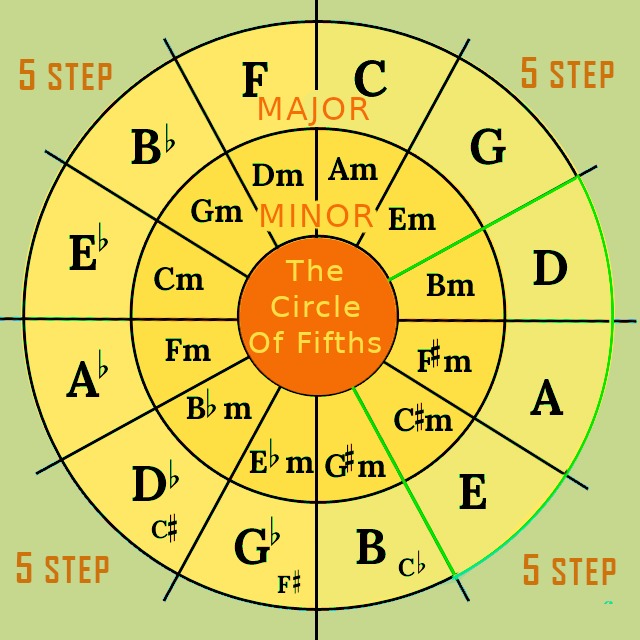
In music, a key is a set of seven notes known as a scale. The scale is built by a specific relationship between the notes. It is the concept of a Circle of Fifths, were imagined the keys on a keyboard are twisted into a circle. The Circle of Fifths is divided up into 12 slices.
You can have the Circle of Fifths having two sections –
It shows the actual key signatures. It says how many sharps or flats (black notes) are in each key. The major keys are on the outside ring of the circle. The capital letters denote the corresponding major keys.
Whereas the relative minor keys of sharps or flats (black notes) are in each key is on the inner ring of the circle.
The key signatures have interval relationships between them, which is why it is called the circle of fifths. A fifth is an interval in music. An interval is a distance between two notes. At the top, C major, which has no sharps or flats in its key signature. Start from C move clockwise for sharps, and anticlockwise for flats.
The interval of 5th will prove now when you start counting from C and go clockwise, will get-
It follows the same pattern of 5th intervals between the notes, and finally ends up or again comes back to the C note, after completing a full circle.
The inner ring follows the same formula, where A will begin the counting, going clockwise with 5 intervals-
It also completes a circle after moving through all 12 notes of the musical alphabet going in 5ths finally returning to a.
Enharmonic notes The two keys are shown because both key signatures are commonly used. At the bottom of the circle, we find a few like B, F♯, and C♯.
Key signatures are unique sequences of sharps, flats, and natural notes in music.
In this concept, another aspect of the circle anticlockwise will see the progression moves by fourths. Fourths are another musical interval.
The notes go in 4ths all the way around the circle when moving anticlockwise or left to right.
The circle of fifths teaches us how many sharps or flats are in each key, and their sequences. Applied to key signatures, notation, and transposition. Through the geometrical structure gives us the overall structure of music. It is used for strong bass line movement. Helps to create great chord progressions. It makes modulating from one key to another much easier. It’s easy to modulate adjacent keys on the left or on right.
In modern music creation in DAW within specific keys, quick programming in melodies, harmonies, bass lines, and chords is possible through the deep knowledge & technique of this circle.
As a songwriter, the Circle of Fifths is a perfect tool in creating memorable melodies by progression by choosing a key and identifying the seven chords that naturally exist in that key.